Rx Pad
Mild Hyperbaric Oxygen vs Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy
What is the difference between
"Mild Hyperbaric Oxygen" vs. "Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy".
The following is given with permission for use of UHMS, Hyperbaric Medicine Indications Manual, 15th Edition granted by Undersea & Hyperbaric Medical, NPB, FL.
Hyperbaric Air and its Potential Unsafe Deliver
Hyperbaric air involves increasing the barometric pressure above normal atmospheric pressure while breath in air. This type of treatment was defined in the medical literature as early as 1662 and has no medical rationale when using pressures less than 2.0 ATA. The chambers delivered hyperbaric air for use as a “medical spa” as one would use a spa today; however, in the 1800s it was being used to support certain medical and surgical conditions without credible research at a time when Evidence Based Medicine (EBM) had not been developed. EBM did not become a standard until 1992 when introduced by Dr. David Sackett. The use of hyperbaric air in history was described by some physicians as having a physiologic basis, mainly when used above 2.0 ATA. Unfortunately, the use of hyperbaric air became a mainstay of many subjective treatments including the Spanish Flu, hypertension, diabetes mellitus, syphilis, and various cancer treatments that patients paid for without sound scientific proof of its efficacy. Those treatments had the added risk of patients suffering adverse effects of breathing hyperbaric air for long exposures.
Unproven Hyperbaric Treatment Often Termed Mild Hyperbaric Oxygen
Mild hyperbaric facilities have proliferated in wellness centers, spas, and even shopping center store fronts. These centers use untested and uncertified chambers that present significant fire risks as well as potential loss of life due to explosive decompressions. Mild hyperbaric facilities are now employing oxygen concentrators to enrich the breathing gas mix in the subtherapeutic chamber pressures they employ. These concentrators are mated to delivery systems (simple oronasal masks or nasal prongs) that are subject to leaks, and the intrusion of ambient gasses results in a breathing mix that is well less than 100% oxygen. Both hyperbaric chambers and oxygen concentrators are Class II medical devices. The FDA requires that both be cleared individually and together for them to be marketed in the United States. Furthermore, these mild hyperbaric centers are using chambers not meeting the standards of the ASME PVHO-1 or the NFPA. As oxygen escapes into the chamber, it creates a significantly enriched oxygen atmosphere, and when it approaches a concentration of 23.5% or higher, it may have potential catastrophic results. The presence of oxygen enhances both the intensity and rapidity of the spread of fire. Many patients purchase these chambers for their home and have no guidance to the potential catastrophic occurrences. Mild hyperbaric facilities typically deliver sessions for an hour or less, for a spectrum of medical disorders or complaints. When the proven and accepted indications for hyperbaric oxygen are treated in these mild hyperbaric chambers, this treatment is inadequate and ineffective. Moreover, these mild hyperbaric centers treat diagnoses for which HBO2has not been found to be clinically effective or listed in this manual’s accepted diagnoses. There is no credible evidence to support the use of mild hyperbaric oxygen for any EBM indication for hyperbaric oxygen as reported in this manual. The application of mild hyperbaric therapy for the treatment of acceptable indications can lead to severe disability or death of the patient or occupant because of inadequate treatment. Mild hyperbaric sessions are offered for many experimental indications for which there is no evidence based scientific support and usually against the healthcare advertising practices of both the Federal Trade Commission (FTC)and Federal Drug Administration (FDA). The target group for these treatments may include children with dis-orders such as autism, cerebral palsy, post concussive/traumatic brain injury syndromes, and near drowning with cerebral anoxia. Also targeted for treatment in mild hyperbaric centers are the elderly patients having suffered cerebrovascular accidents (strokes) or those with cognitive decline. Since medical insurers do not reimburse forth ese experimental indications, patients are provided with a substantial out of pocket expense.
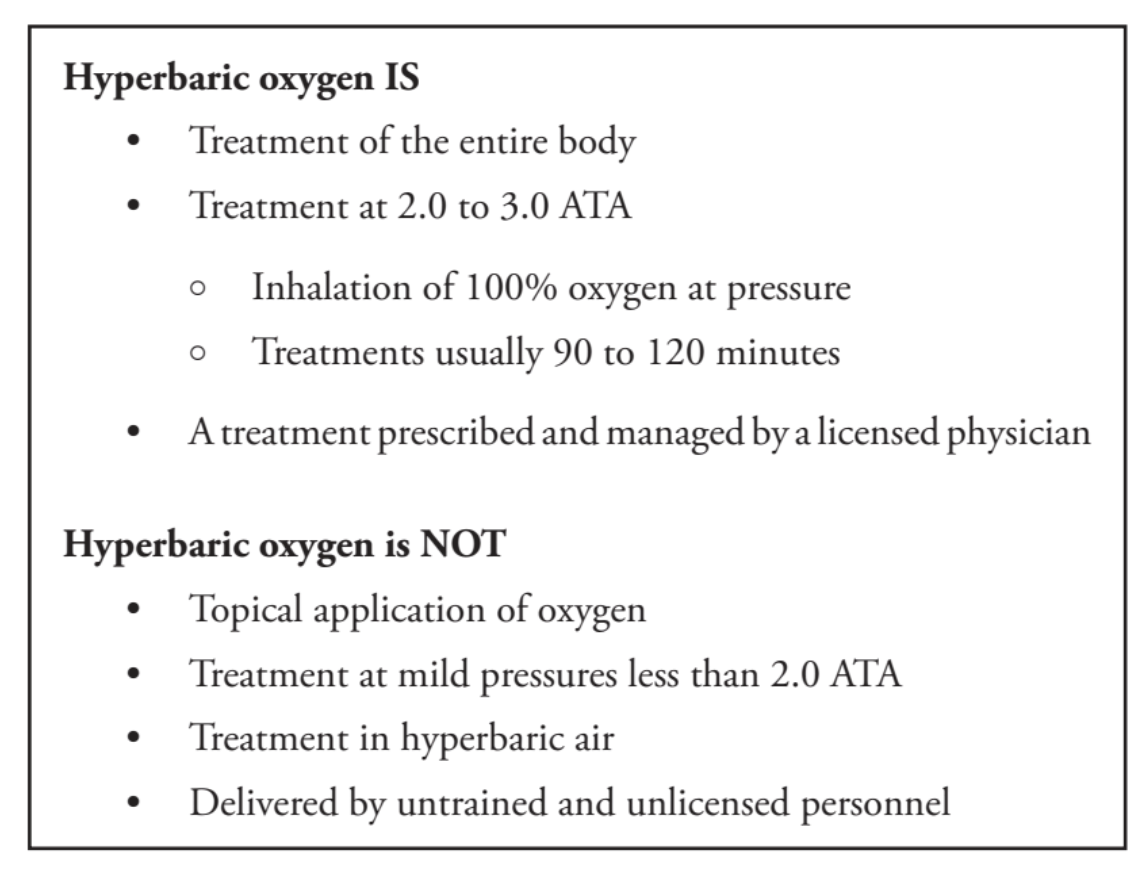
Definition of Hyperbaric Oxygen and its Safe Delivery
The definition of clinical HBO2 is complex and often misrepresented to justify its use for unproven treatments. For this reason and to clarify misunderstandings, the UHMS Hyperbaric Medicine Committee has defined what a session of HBO2 must include.
Hyperbaric oxygen is a medical procedure requiring a physician’s prescription and oversight. All patients must have their entire body placed within a hard sided hyperbaric chamber that meets the American Society of Mechanical Engineers and Pressure Vessels for Human Occupancy (ASME-PVHO-1) code, and the National Fire Protection Association (NFPA99) code and standards for hyperbaric chambers, at a pressure of not less than 2.0 ATA (202.65 KPa) while breathing physician prescribed medical grade oxygen for an amount of time that is typically between 90-120 minutes per treatment. Medical grade oxygen (>99.0% oxygen purity) is the only acceptable gas that should be used for therapeutic delivery of hyperbaric oxygen.
During appropriate and acceptable clinical hyperbaric use, oxygen acts as a drug and is regulated by the FDA. Using Evidence Based Medicine (EBM) criteria, HBO2is dosed systemically by breathing medical grade oxygen under increased hyperbaric pressure, for the diagnoses described in this manual and approved by the Undersea Hyperbaric Medical Society (UHMS).
UNDERSEA HYPERBARIC MEDICAL SOCIETY
The Continuing Medical Education mission of UHMS is to develop and promote evidence-based educational activities that improve the scientific knowledge, competence and/or performance within the scope of undersea and hyperbaric medicine, including wound healing. For more information please go to: UHMS.org.
ABOUT THE TEXT: UHMS INDICATIONS 15th Edition
Since its first appearance in 1977, the UHMS Hyperbaric Medicine Indications Manual has served as a guide for practitioners and scientists interested in hyperbaric and undersea medicine. For your copy of UHMS Indications 15th Edition pleae go to BestPub.com.
EDUCATION FOR HYPERBARIC MEDICINE
Wound Care Education Partners and the Hyperbaric Certification Commission provide leducational resources for medical professionals and hyperbaric facility staff and directors. These live courses and certifications provide continuing education credits and foundation knowledge & skills from leaders in the industry. Follow the links above below for more informaiton.
When you subscribe to the blog, we will send you an e-mail when there are new updates on the site so you wouldn't miss them.



Comments